Swanson's Law on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
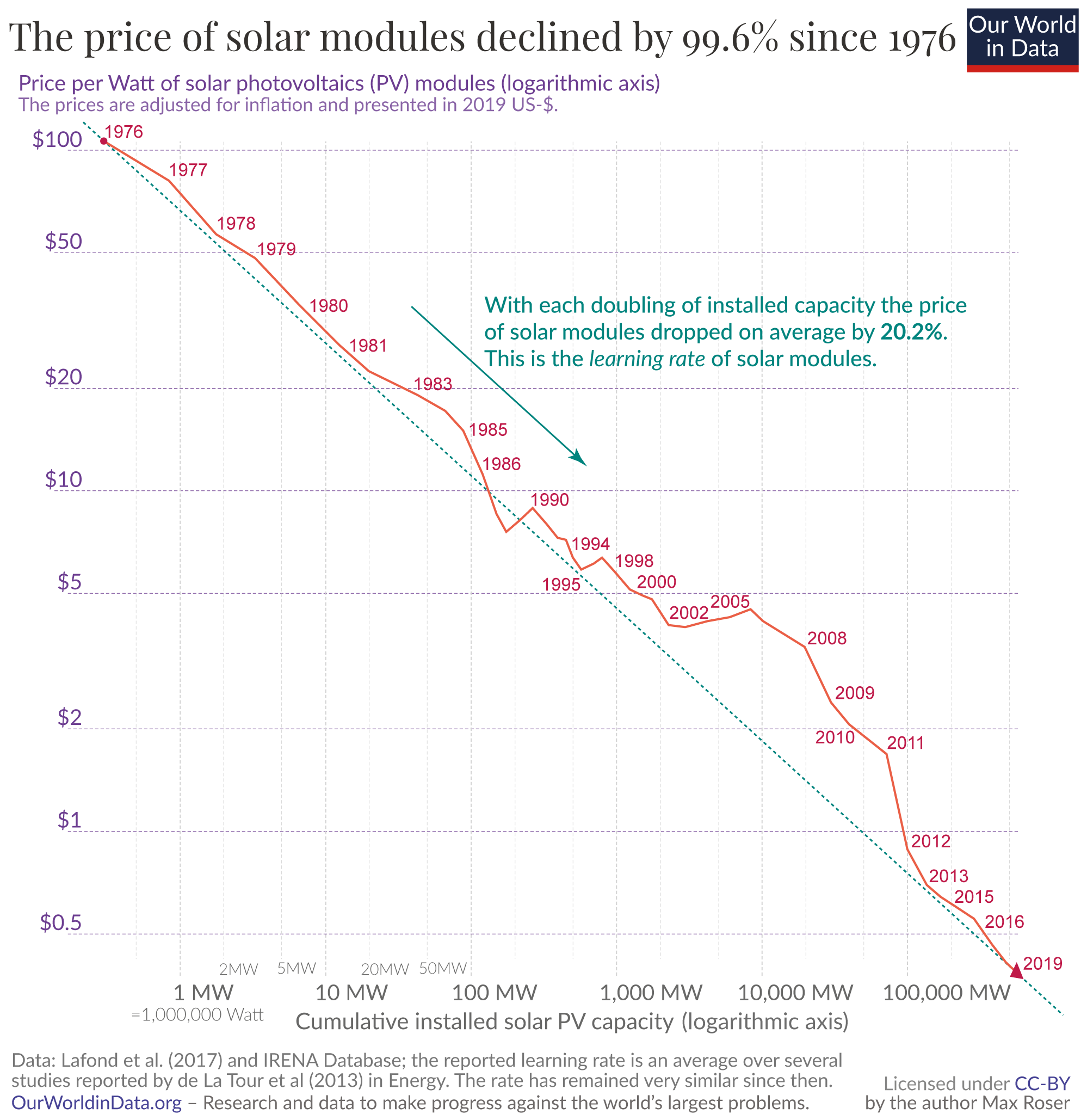 Swanson's law is the observation that the price of solar
Swanson's law is the observation that the price of solar
 Swanson's law is the observation that the price of solar
Swanson's law is the observation that the price of solar photovoltaic module
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially us ...
s tends to drop 20 percent for every doubling of cumulative shipped volume. At present rates, costs go down 75% about every 10 years.
Origin
It is named after Richard Swanson, the founder of SunPower Corporation, a solar panel manufacturer. Note: Read more about current innovations in solar technology. The term ''Swanson's Law'' appears to have originated with an article in ''The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British weekly newspaper printed in demitab format and published digitally. It focuses on current affairs, international business, politics, technology, and culture. Based in London, the newspaper is owned by The Econo ...
'' published in late 2012. Swanson had been presenting such curves at technical conferences for several years. It is a misnomer
A misnomer is a name that is incorrectly or unsuitably applied. Misnomers often arise because something was named long before its correct nature was known, or because an earlier form of something has been replaced by a later form to which the name ...
in that Swanson was not the first person to make this observation.
Swanson's law has been compared to Moore's law
Moore's law is the observation that the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empir ...
, which predicts the growing computing power of processors. Swanson's Law is a solar industry specific application of the more general Wright's Law which states there will be a fixed cost reduction for each doubling of manufacturing volume.
Technical Background
The method used by Swanson is more commonly referred to as ''learning curve
A learning curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between how Skill, proficient people are at a task and the amount of experience they have. Proficiency (measured on the vertical axis) usually increases with increased experience ...
'' or more precise '' experience curve'' analysis. It was first developed and applied to the aeronautics industry in 1936 by Theodore Paul Wright
Theodore Paul Wright (May 25, 1895 – August 21, 1970), also known as T. P. Wright, was a U.S. aeronautical engineer and educator.
Biography
He was born in Galesburg, Illinois on May 25, 1895. His father was the economist Philip Green Wri ...
. There are reports of it first being applied to the photovoltaics industry in 1975, and saw wider use starting in the early 1990s.
Crystalline silicon
Crystalline silicon or (c-Si) Is the crystalline forms of silicon, either polycrystalline silicon (poly-Si, consisting of small crystals), or monocrystalline silicon (mono-Si, a continuous crystal). Crystalline silicon is the dominant semicondu ...
photovoltaic cell prices have fallen from $76.67 per watt in 1977 to $0.36 per watt in 2014. Plotting the module price (in $/Wp) versus time shows a dropping by 10% per year. License: cc. Note: Appendix F. A trend extrapolation of solar energy capacity.
See also
*Economies of scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of output produced per unit of time. A decrease in cost per unit of output enables ...
* Growth of photovoltaics
Worldwide growth of photovoltaics has been close to exponential between 1992 and 2018.
During this period of time, photovoltaics (PV), also known as solar PV, evolved from a niche market of small-scale applications to a mainstream electricit ...
* Learning curve
A learning curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between how Skill, proficient people are at a task and the amount of experience they have. Proficiency (measured on the vertical axis) usually increases with increased experience ...
* Log–log plot
In science and engineering, a log–log graph or log–log plot is a two-dimensional graph of numerical data that uses logarithmic scales on both the horizontal and vertical axes. Power functions – relationships of the form y=ax^k – appear as ...
* Moore's law
Moore's law is the observation that the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empir ...
* Photovoltaic system
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and co ...
* Wright's Law
References
{{reflist Photovoltaics Rules of thumb